
Inner Ear Problems Causes & Treatment of inner ear Dizziness & Vertigo
The fluid inside the cochlea, which is a spiral-shaped, fluid-filled structure in the inner ear, is called perilymph. Perilymph is one of the two types of fluid found in the cochlea, the other being endolymph. These fluids play a crucial role in the process of hearing by transmitting sound vibrations and stimulating the hair cells in the cochlea.

Ear Anatomy Vestibular Disorders Association
The Anatomy of the Ear LEONELLO CALVETTI / Getty Images Anatomy Structure The ear is made up of the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The inner ear consists of the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth comprises three components:
Ear Anatomy Causes of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
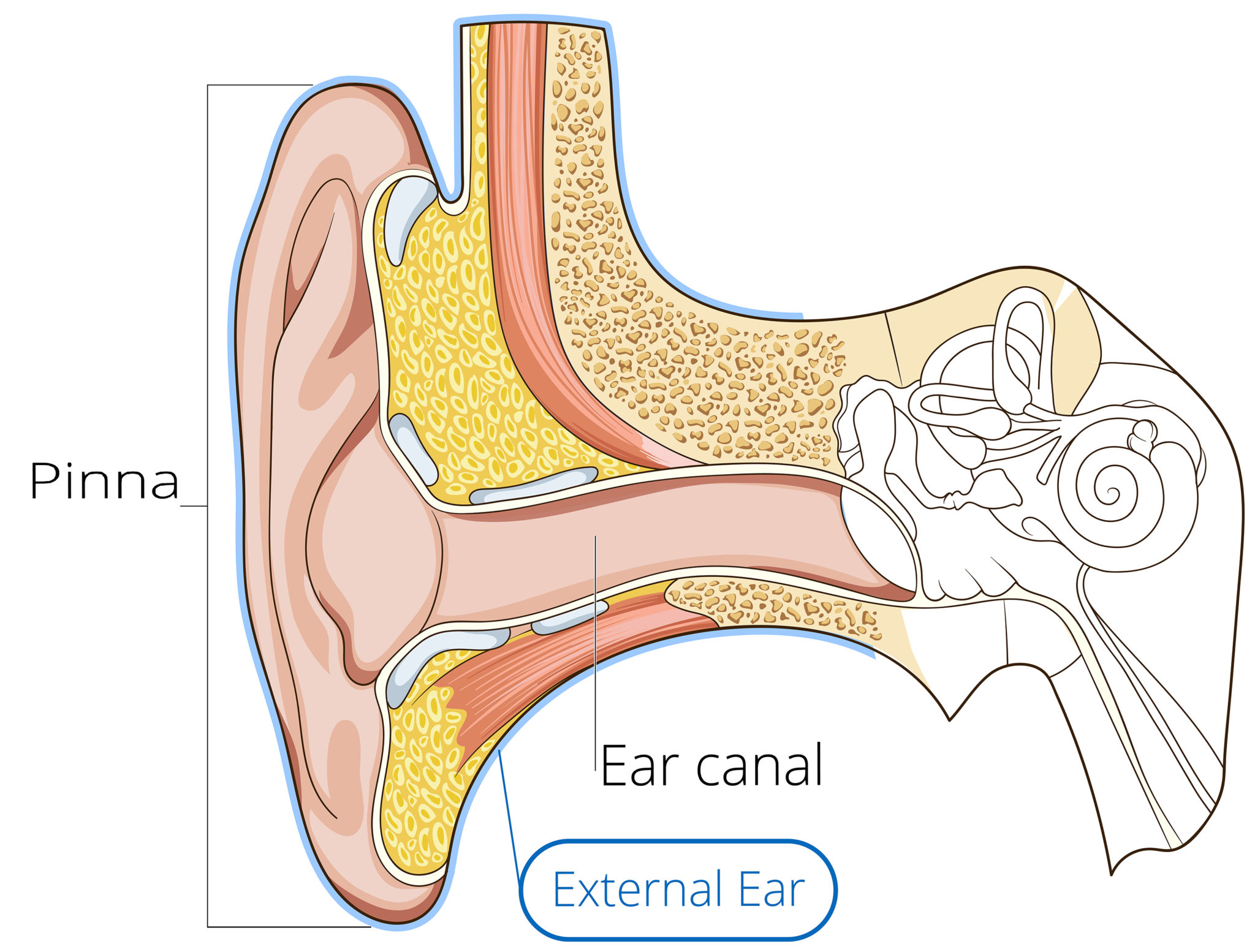
Reading time: 40 minutes Recommended video: Introduction to the ear [21:34] Overview of the structures of the outer ear and auditory tube. External acoustic meatus Meatus acusticus externus 1/4 Synonyms: External auditory meatus, External acoustic pore , show more. The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system.

Vertigo Have You Spinning Chiropractic Home Care Ear anatomy, Human
Labelled Diagram of Inner Ear Inner Ear - Description The inner ear or labyrinth of the human ear comprises 2 structures - the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. Bony labyrinth is a series of cavities or channels present in the petrous part of the temporal bone. The membranous labyrinth is present within the bony labyrinth.

Alila Medical Media Human ear anatomy, labeled diagram. Medical
Ear Anatomy, Diagram & Pictures | Body Maps Human body Head Ear Ear The ears are organs that provide two main functions — hearing and balance — that depend on specialized receptors called.

Inner Ear Problems Causes & Treatment of inner ear Dizziness & Vertigo
The inner ear, known as the labyrinth, contains two primary structures: the cochlea, responsible for hearing, and the vestibular apparatus, responsible for maintaining balance, stability and spatial orientation. The labyrinth, or inner ear (see figure 1) is encased in bone, called the bony labyrinth. Suspended by fluid (perilymph) within the.
SPEECH LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY & AUDIOLOGY HEARING DISORDERS OF THE OUTER EAR
Inner and Middle Ear. The cochlea is the most critical component of the inner ear. It is divided into three fluid-filled chambers, called scalae, that spiral around a bony core. The scala media.

Diagram of the anatomy of the ear Ear diagram, Human ear, Ear anatomy
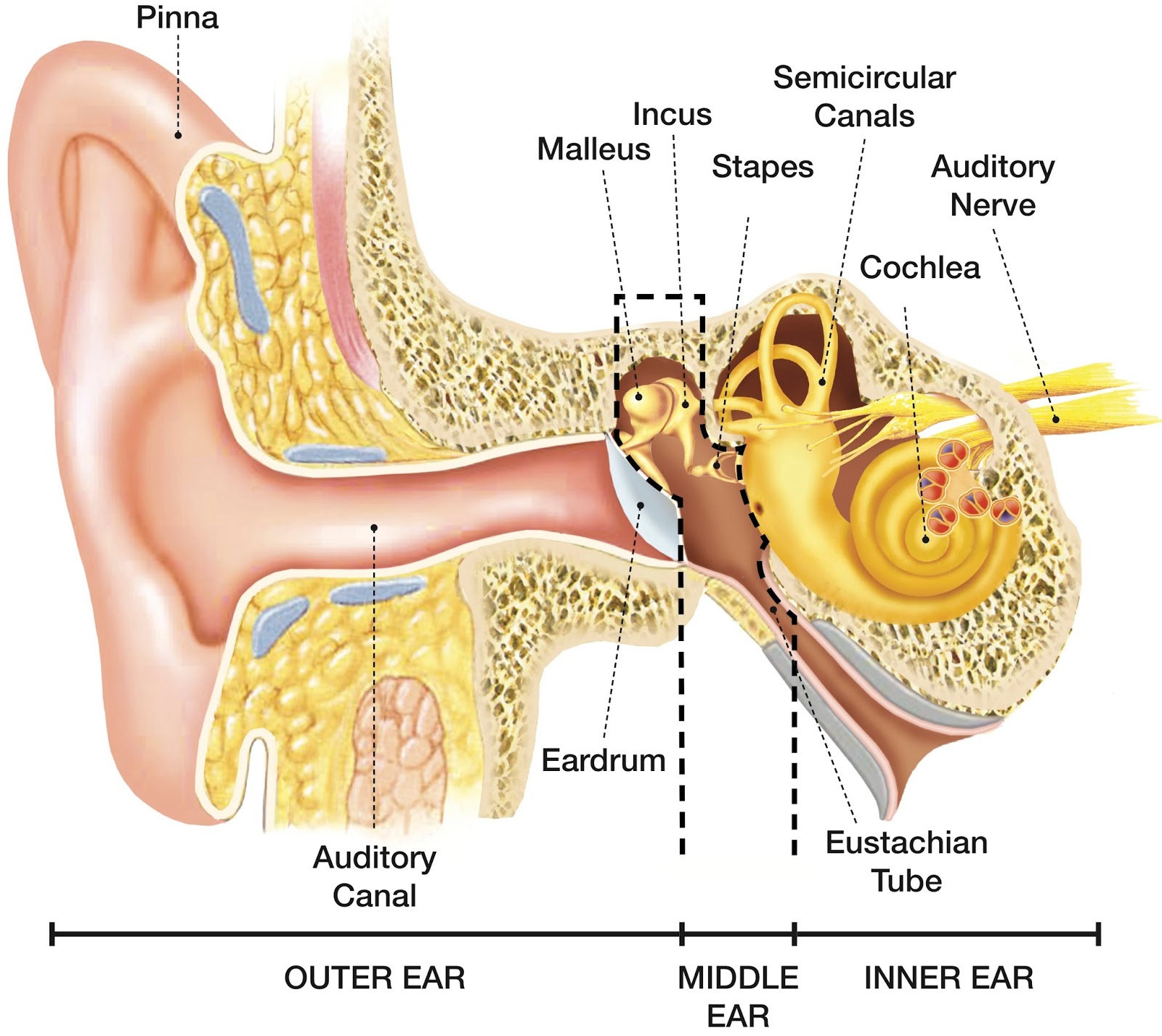
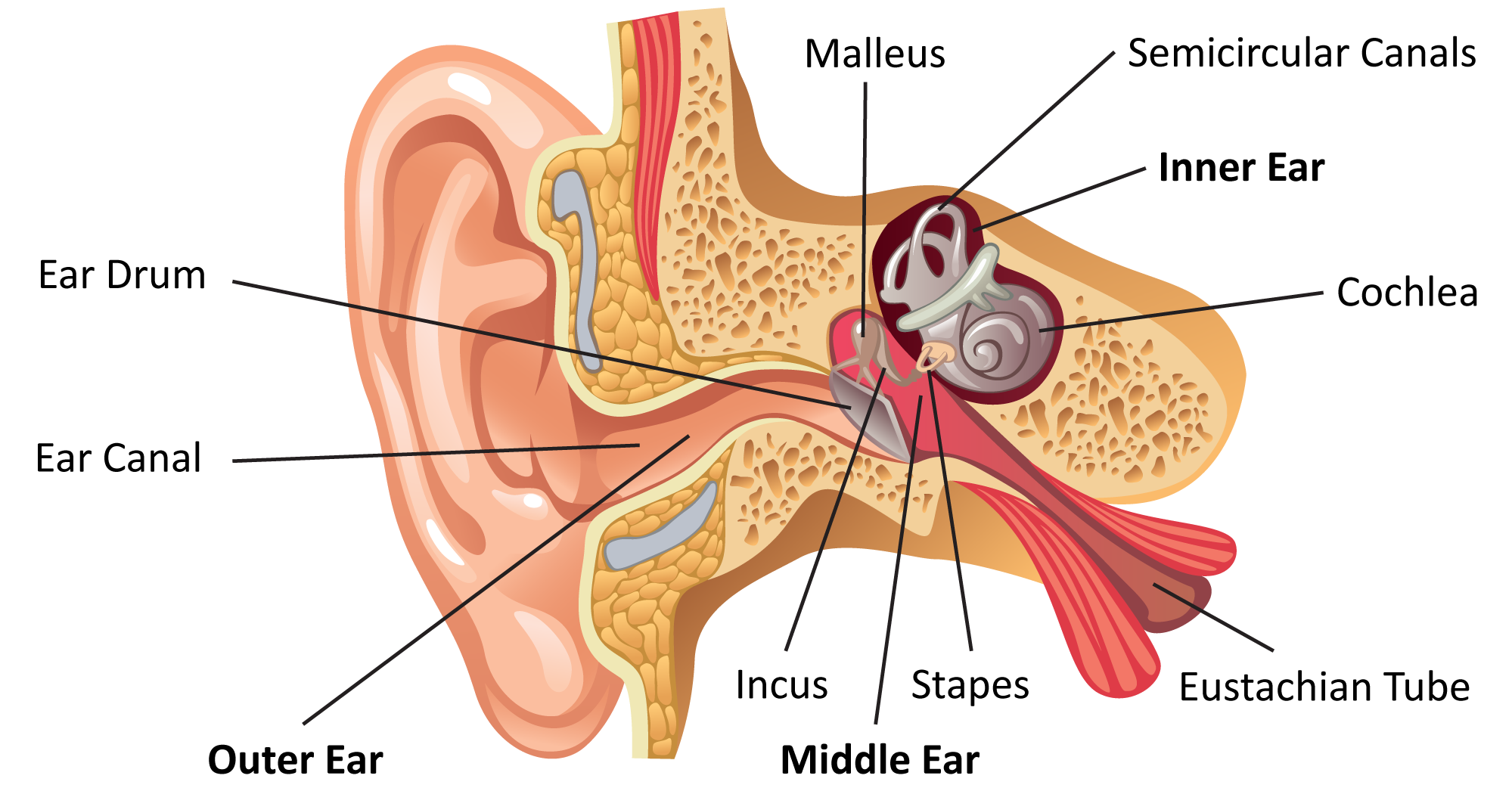
What is the inner ear? What we think of as the "ear" is actually a three-part structure. The outer ear is the part you see and your ear canal. The middle ear is a box-shaped area behind the tympanic membrane (eardrum) that includes the three smallest bones in your body.

utricle Google Search EarWaxBuildup Inner ear diagram, Inner ear
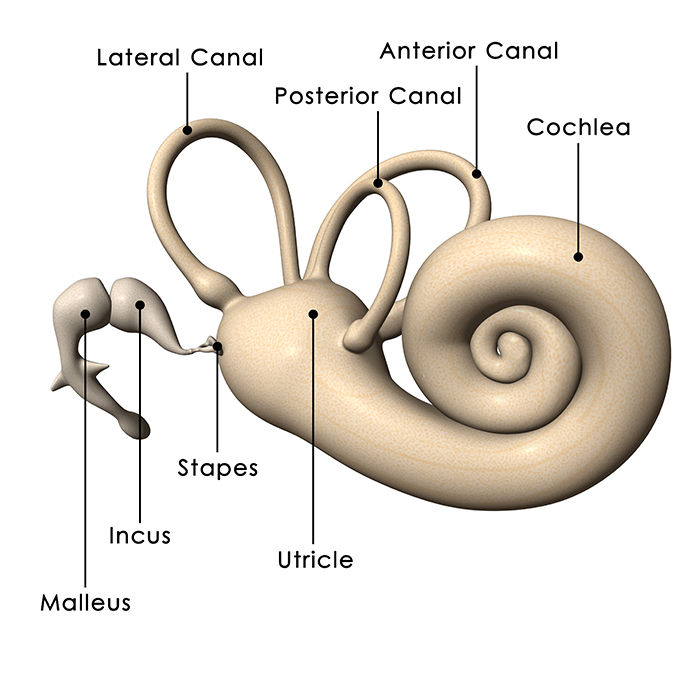
Anatomy. The inner ear is a complex three dimensional shape with semicircular canals, dilations called the utricle and saccule and a spiral portion known as the cochlea. All of these organs are housed inside a bony shell known as the bony labyrinth and this is within the temporal bone. The cochlea is the site where sound is transformed into.
We Finally Know Why There's a Bizarre Structure in Our Inner Ears
The inner ear is the innermost part of the ear and consists of the cochlea, auditory nerve, vestibule and semicircular canals. The inner ear is a maze of tubes and passages, referred to as the labyrinth. The inner ear is mainly responsible for balance and detecting sound. The cochlea contains the cells responsible for hearing, the auditory.
How We Perceive Sound
Ear Anatomy - Inner Ear. Ear Anatomy Schematics. Ear Anatomy Images. Chapter 4 - Fluid in the ear. Fluid in the ear Discussion. Fluid in the ear Outline. Middle Ear Ventilation Tubes. Fluid in the ear Images. Chapter 5 - Traveler's Ear.
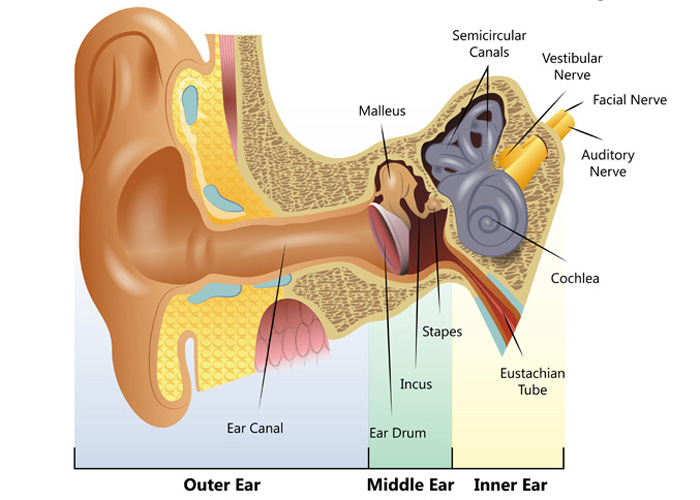
Common balance disorders Hearing Link
human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance (equilibrium). Understand the science of hearing and how humans and other mammals perceive sound How humans and other mammals perceive sound.

Human ear anatomy. Ears inner structure, organ of hearing ve (1000410
Inner Ear Anatomy. The inner ear is where the sound waves are translated into types of electrical nerve impulses. Most of the hearing and balance content is located within the bony labyrinth. After the tympanic membrane, these are the nerves that most likely contribute to hearing impairment and may require treatment or medical services [1].
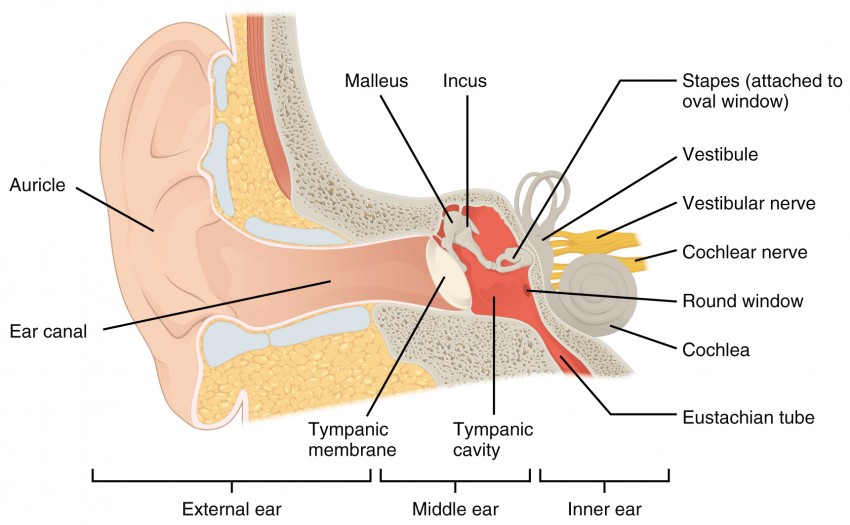
Audition and Somatosensation Anatomy and Physiology I
Overview Your outer ear and middle ear are separated by your eardrum, and your inner ear houses the cochlea, vestibular nerve and semicircular canals (fluid-filled spaces involved in balance and hearing). What is the ear? Your ears are organs that detect and analyze sound. Located on each side of your head, they help with hearing and balance.
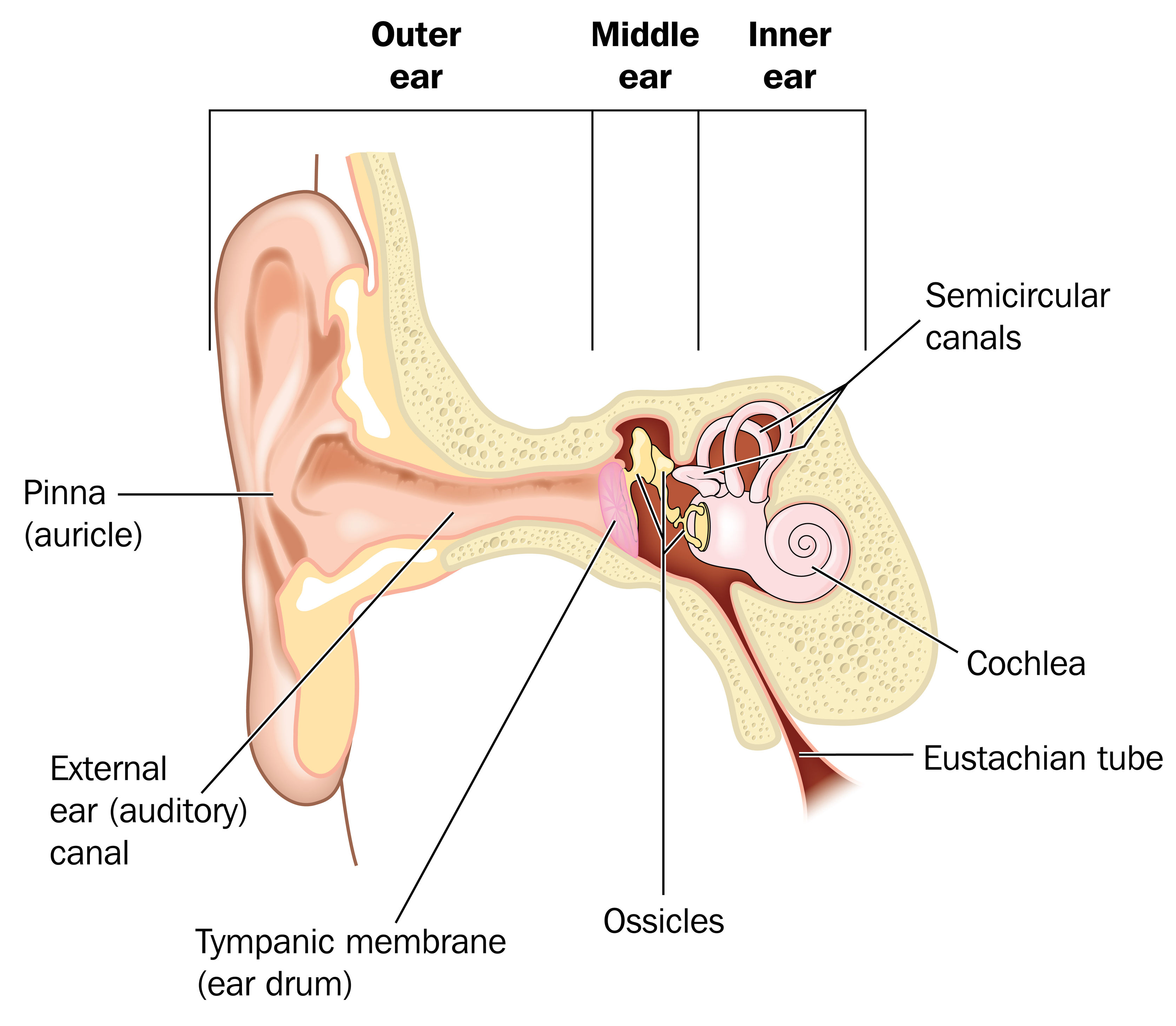
Ear infections explained Dr Mark McGrath
Inner ear anatomy. The outer, middle, and inner ear. The inner ear is at the end of the ear tubes. It sits in a small hole-like cavity in the skull bones on both sides of the head. The inner ear.

Hearing Loss Regenerated in Damaged Mammal Ear The Personal Longevity
Ear Anatomy - Inner Ear Next to the middle ear in the bone of the skull is a small compartment which contains the hearing and balance apparatus known as the inner ear. The inner ear has two main parts. The cochlea , which is the hearing portion, and the semicircular canals is the balance portion.